Factory Supply Aniline Icis - Aniline CAS 62-53-3 China Best Price – Chemwin Detail:
Product Name:Aniline
Molecular format:C6H7N
CAS No:62-53-3
Product molecular structure:
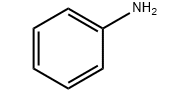
Chemical Properties:
Aniline is the simplest primary aromatic amine and a compound formed by the substitution of a hydrogen atom in the benzene molecule with an amino group. It is colorless oil like flammable liquid with strong odor. When heated to 370 C, it is slightly soluble in water and soluble in ethanol, ether, chloroform and other organic solvents. It becomes brown in the air or under the sun. It can be distilled by steam. A small amount of zinc powder is added to prevent oxidation when it is distilled. The purified aniline can be added 10 ~ 15ppm NaBH4 to prevent oxidation deterioration. The solution of aniline is alkaline.
It is easy to produce salt when it reacts with acid. The hydrogen atoms on its amino groups can be substituted by alkyl or acyl groups to produce second or third grade aniline and acyl aniline. When substitution reaction occurs, the products of ortho and para substituted products are mainly produced. It reacts with nitrite to form diazonium salts, which can be used to produce a series of benzene derivatives and azo compounds.
Application:
Aniline is predominantly used as a chemical intermediate for dyes, drugs, explosives, plastics, and photographic and rubber chemicals. Many chemicals can be made from Aniline, including:
Isocyanaates for the urethane industry
Antioxidants, activators, accelerators, and other chemicals for the rubber industry
Indigo, acetoacetanilide, and other dyes and pigments for a variety of applications
Diphenylamine for the rubber, petroleum, plastics, agricultural, explosives, and chemical industries
Various fungacides and herbicides for the agricultural industry
Pharmaceutical, organic chemical, and other products
Product detail pictures:

Related Product Guide:
We always follow the principle Quality Very first, Prestige Supreme. We have been fully committed to delivering our customers with competitively priced high-quality products and solutions, prompt delivery and experienced services for Factory Supply Aniline Icis - Aniline CAS 62-53-3 China Best Price – Chemwin , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Italy, Cambodia, Rotterdam, With high quality, reasonable price, on-time delivery and customized & personalized services to help customers achieve their goals successfully, our company has got praise in both domestic and foreign markets. Buyers are welcome to contact us.
Production management mechanism is completed, quality is guaranteed, high credibility and service let the cooperation is easy, perfect!
Products categories
-

Phone
-

E-mail
-

Whatsapp
-

Top








